Explore the functionality of cutting-edge AI agents and their practical applications. Embark on your journey into the world of AI applications today!
The rapid progression of AI has introduced the concept of AI agents. These intelligent entities are integral in diverse domains, serving as virtual customer service agents and formidable data-gathering powerhouses, all autonomously operating without human intervention. This article delves into the intricacies of AI agents, examining their significance in complex environments.
What are AI agents?
AI agents are entities crafted to comprehend their surroundings and enact actions to accomplish specific objectives. These agents may manifest as software-based programs or physical entities, typically constructed employing artificial intelligence techniques. They interpret their surroundings through sensors, process information using algorithms or models, and subsequently execute actions via actuators or other mechanisms.
AI agents exhibit a spectrum of complexity, ranging from straightforward systems adhering to predefined rules to intricate, autonomous entities capable of learning and adapting from experiences. Their applications span various fields, including robotics, gaming, virtual assistants, autonomous vehicles, and more. These agents can assume different roles, such as reactive (responding directly to stimuli), deliberative (planning and decision-making), or possessing learning capabilities (adapting behavior based on data and experiences).
Read more: Custom AI Model: Build or Buy? Choosing the Best Option for Your Business
Developing Agent Programs with Natural Language Processing for Rationality
Natural Language Processing (NLP) falls under the domain of artificial intelligence, concentrating on the interaction between humans and computers through natural language. It encompasses the creation of algorithms and models to empower computers to comprehend, interpret, and generate human language. NLP proves indispensable in a variety of AI applications, spanning chatbots, language translation, sentiment analysis, and text summarization.
Machine learning models, notably those employing deep learning techniques, assume a crucial role in NLP. These models can discern patterns and relationships within language data, enabling AI agents to generalize and make sense of new, unseen language. Trained on extensive corpora of text data, these models achieve an understanding of language, allowing them to generate text with human-like fluency and accuracy.
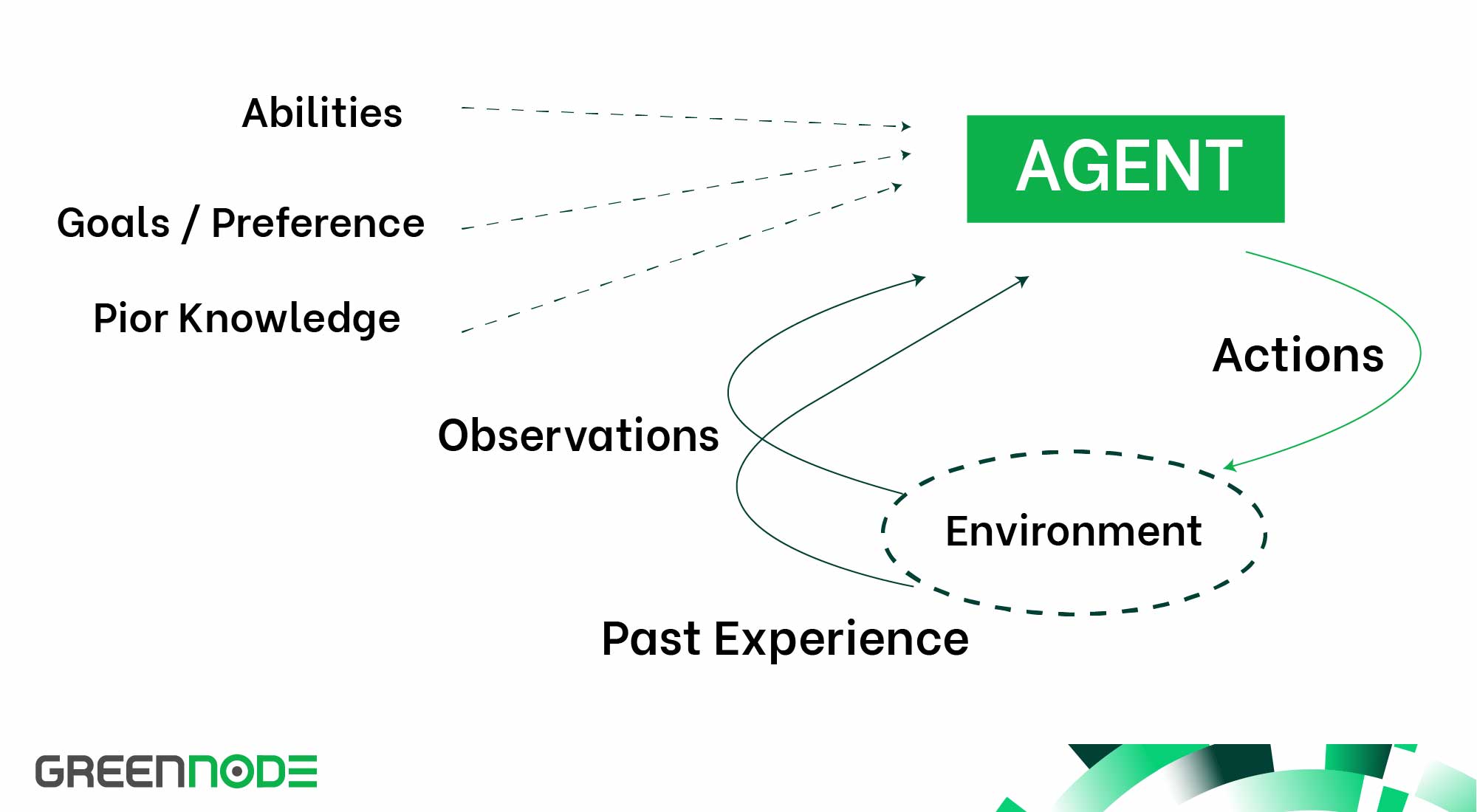
The Components of an AI Agent
Various components collaborate to empower an AI agent to function effectively within its environment. These components are pivotal for crafting intelligent agents capable of autonomously executing tasks across diverse applications.

Agent Function
At the core of an AI agent lies its agent function. This component defines how the agent translates the data it gathers into actions. In simpler terms, the agent function empowers the AI to discern appropriate actions based on the acquired information. This is where the "intelligence" of the agent resides, involving reasoning and the selection of actions to fulfil its objectives.
Percepts
Percepts represent the sensory inputs that the AI agent receives from its surroundings. They furnish information about the current state of the observable environment in which the agent operates. For instance, in the case of a customer service chatbot, percepts may encompass:
- User Messages
- User Profile Information
- User Location
- Chat History
- Language Preferences
- Time and Date
- User Preferences
- User Emotion Recognition
Actuators
Actuators function as the operational "muscles" of the agent, carrying out the decisions formulated by the agent function. These actions encompass a broad spectrum of tasks, ranging from guiding a self-driving car to inputting text on a screen for a chatbot.
Some prevalent actuators include:
- Text Response Generator: This actuator is responsible for creating and dispatching text-based responses to the user. It takes the chatbot's textual reply and conveys it to the user through the chat interface.
- Service Integration APIs: In scenarios where a chatbot needs to integrate with systems such as the company's CRM system to access customer data, create support tickets, or check order statuses, service integration APIs serve as actuators. They enable the chatbot to interact with external systems, retrieving or updating information as required.
- Notification and Alerts: Actuators designed for notifications can send alerts via email, SMS, or push notifications to the user's device. These notifications inform users about upcoming appointments, changes in order status, promotions, or other pertinent updates, contributing to user engagement.
Knowledge Base
The knowledge base serves as the repository where the AI agent stores its initial knowledge about the environment. This knowledge is typically pre-defined or acquired during training, forming the bedrock for the agent's decision-making process. For example, a self-driving car might possess a knowledge base containing information about road rules. At the same time, a customer service agent's autonomous counterpart may access detailed data about a company's products.
Feedback
Feedback is imperative for the continual improvement of the AI agent. This feedback can originate from two sources: a critic or the environment itself. The critic may be a human operator, or another AI system tasked with evaluating the agent's performance. Alternatively, the environment can offer feedback through outcomes resulting from the agent's actions. This feedback loop enables agents to adapt, learn from experiences, and enhance decision-making capabilities over time.
Types of AI Agents
- Reactive Agents: Operating on predefined condition-action rules, these agents respond solely to the current percept without considering the history of previous percepts. They excel in tasks with limited complexity and a narrow scope of capabilities.
- Model-Based Reflex Agents: Taking a more sophisticated approach, these agents maintain an internal model of the environment, allowing them to make decisions based on a broader understanding. This capability makes them adept at handling more complex tasks.
- Utility-Based Agents: Decision-making for utility-based agents revolves around evaluating the expected utility of each potential action. They are particularly valuable in scenarios where weighing various options and selecting the one with the highest expected utility is crucial.
- Learning Agents: Designed for unknown environments, learning agents evolve by learning from experiences and adjusting their actions over time. The development of learning agents often involves the incorporation of deep learning and neural networks.
- Belief-Desire-Intention Agents: Modeling human-like behavior, these agents maintain beliefs about the environment, desires, and intentions. Their ability to reason and plan actions makes them well-suited for handling complex systems.
- Logic-Based Agents: Relying on deductive reasoning and logic rules, these agents excel in tasks demanding intricate logical reasoning.

What Are AI Agent Platforms?
AI agent platforms are software environments that allow users to build, deploy, and manage autonomous AI agents, intelligent systems capable of reasoning, planning, and taking actions independently. These platforms form the backbone of modern automation and AI-driven workflows, enabling businesses to go beyond traditional chatbots or scripted assistants.
In essence, an AI agent platform serves as the foundation for building intelligent digital agents that can interact with data, tools, and applications in real time. It provides the infrastructure such as language model integration, memory, APIs, and orchestration frameworks that allows AI agents to understand goals, make decisions, and act on behalf of users or organizations.
Modern AI agent platforms combine the power of large language models (LLMs) with reasoning frameworks and integration layers. This combination allows an AI agent to not only respond to text but also take action within software ecosystems, for example, sending emails, querying databases, or running analytical tasks. Unlike conventional automation tools, these platforms empower agents to learn from interactions and adapt over time.
Most AI agent platforms share five key components that define their functionality:
Language Model Integration – Connects to LLMs such as GPT-4, Claude, or Gemini to enable reasoning and natural language understanding.
Memory and Context – Stores interaction history or business data so agents can maintain context across sessions.
Tool Access – Allows agents to use APIs, databases, or external apps to complete tasks.
Orchestration Engine – Manages how multiple agents collaborate, prioritize tasks, and resolve dependencies.
Governance and Monitoring – Ensures safe, compliant, and trackable operation of AI agents in enterprise environments.
Best AI Agent Platforms to Know in 2025
The rise of AI agent platforms marks a major shift in how organizations build intelligent systems. Rather than coding isolated assistants or chatbots, businesses now rely on unified platforms that provide everything — from reasoning and orchestration to integration, memory, and monitoring. In 2025, several AI agent platforms stand out for their innovation, scalability, and developer adoption.
Below are the top AI agent platforms shaping the future of autonomous AI applications.
LangChain
LangChain is one of the most influential open-source AI agent frameworks. It enables developers to create complex, multi-step agents that can reason, plan, and interact with APIs, databases, or external systems. Built around modular “chains,” LangChain provides the foundation for custom AI agent platforms and has become the go-to choice for developers building with OpenAI, Anthropic, or open-source LLMs.
Why it stands out:
LangChain is ideal for teams that want full control over their agent’s reasoning logic and integrations. Its extensive ecosystem of tools, templates, and community plugins supports rapid experimentation and deployment.
Best for: Developers, startups, and R&D teams building custom, code-based AI agent solutions.
LlamaIndex (formerly GPT Index)
LlamaIndex specializes in connecting AI agents to private or enterprise data sources. It focuses on the retrieval and reasoning layer of AI agent platforms, allowing agents to access structured and unstructured data from documents, APIs, or databases. Combined with LangChain, it’s often used in Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipelines.
Why it stands out:
LlamaIndex excels at managing context and memory for enterprise use cases. It helps AI agents move beyond public knowledge to reason over business-specific data.
Best for: Organizations building data-aware agents, internal knowledge assistants, or RAG systems.
CrewAI
CrewAI is an emerging AI agent platform designed around multi-agent collaboration. It allows users to create “teams” of agents — each with defined roles, goals, and skills — that can cooperate to solve complex tasks. CrewAI manages orchestration, communication, and decision coordination between multiple agents in real time.
Why it stands out:
It simplifies multi-agent system design, enabling developers to scale from a single assistant to a network of specialized AI agents.
Best for: Enterprises and startups experimenting with multi-agent workflows such as automated research, customer operations, or data analysis.
Microsoft Copilot Studio
Microsoft Copilot Studio extends the Microsoft 365 and Azure ecosystems with no-code tools for building custom AI agent platforms. It integrates with Power Automate and Azure OpenAI, enabling organizations to create assistants that perform specific tasks across productivity apps and enterprise workflows.
Why it stands out:
It bridges AI reasoning and real business tools, allowing companies to build copilots that interact with Outlook, Teams, and Dynamics.
Best for: Enterprises already invested in Microsoft infrastructure seeking secure, low-code AI automation.
OpenAI GPTs & Custom GPT Platform
OpenAI’s GPTs allow users to build tailored AI agents through natural language configuration. With the 2024 launch of the GPT Store, these customizable agents form one of the most accessible AI agent platforms for creators and professionals.
Why it stands out:
No programming required, anyone can create agents that retrieve data, access APIs, and perform tasks through the ChatGPT interface.
Best for: Entrepreneurs, educators, and teams wanting fast, no-code deployment of specialized AI agents.
Hugging Face Agents & Transformers Ecosystem
Hugging Face continues to expand its open ecosystem with agent frameworks that integrate directly with its Transformers library. It supports a wide range of LLMs and multimodal models, making it a strong base for developers looking to create transparent, open-source AI agent platforms.
Why it stands out:
Community-driven development, model flexibility, and open collaboration tools make Hugging Face ideal for research and innovation.
Best for: Academic labs, AI startups, and open-source contributors building transparent agent systems.
Potential Applications of AI Agents
AI agents exhibit a wide range of applications across diverse industries, contributing to various functionalities and advancements:
- Autonomous Vehicles: AI agents empower self-driving cars and drones, enabling them to perceive their environment, make decisions, and navigate safely without human intervention.
- Virtual Assistants: Agents like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant leverage AI to comprehend natural language, assist with tasks, provide information, and control smart devices.
- Gaming: AI agents in games simulate human-like behavior, enhancing player experience and delivering challenging opponents in both single-player and multiplayer settings.
- Healthcare: AI agents contribute to diagnostics, personalized medicine, drug discovery, and patient monitoring, improving treatment outcomes and operational efficiency.
- Finance: AI agents analyze extensive financial data for fraud detection, trading, risk assessment, and personalized financial advice.
- Customer Service: Chatbots and virtual agents handle customer queries, offering support, guiding purchases, and providing information across various industries.
- Smart Homes and IoT: AI agents control and optimize smart home devices, adjusting settings based on preferences and environmental conditions.
- Robotics: AI agents in robots enable them to perform tasks in manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and more, adapting to dynamic environments.
- Recommendation Systems: AI agents power recommendation engines in streaming services, e-commerce, and content platforms, offering personalized suggestions to users.
- Cybersecurity: AI agents aid in threat detection, anomaly identification, and security management, defending against cyber attacks and ensuring system integrity.
- Education: AI agents assist in personalized learning, adapting to individual student needs and providing tutoring and educational support.
- Supply Chain and Logistics: AI agents optimize routes, manage inventory, predict demand, and enhance overall efficiency in logistics operations.
These applications underscore the versatility and impact of AI agents in transforming industries, enhancing efficiency, and facilitating innovative solutions across a multitude of domains.
Emerging Trends in AI Agent Technology
AI agents stand at the forefront of artificial intelligence, significantly influencing the way we engage with technology daily. Their capacity to make informed decisions, adapt to changing environments and learn over time positions AI agents as the driving force behind the evolution of intelligent systems set to enhance our everyday experiences.
As technological progress unfolds, AI agents are evolving into more sophisticated and capable entities. Their potential to revolutionize our interactions with intelligent systems is increasingly evident. Frameworks like the GPT architecture for AI agents provide robust tools, enabling the construction and customization of intelligent agents tailored for diverse applications.
Embark on your custom AI journey with GreenNode
At GreenNode, we are dedicated to supporting enterprises in achieving their AI ambitions and timelines, providing top-notch support every step of the way. Join us as we elevate your AI experience and propel your business into the future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About AI Agent Platforms
1. What is an AI agent platform?
An AI agent platform is a software framework that allows developers or organizations to build, deploy, and manage autonomous AI agents. These agents can understand context, make decisions, and take actions within digital environments. Unlike simple chatbots, AI agent platforms provide the full infrastructure, including reasoning, memory, tool integration, and orchestration, needed for intelligent, goal-driven automation.
2. How do AI agent platforms work?
AI agent platforms combine multiple technologies to enable autonomy. They connect large language models (LLMs) like GPT-4 or Claude with reasoning frameworks, APIs, and data systems. The platform coordinates how the agent perceives input, plans actions, executes tasks, and learns from results. In enterprise settings, these platforms often include security, monitoring, and compliance layers to ensure reliability at scale.
3. What are the main components of an AI agent platform?
Most AI agent platforms include:
- Language model integration – connects to foundation models for reasoning.
- Tool and API access – lets agents perform actions (e.g., retrieve data, send emails).
- Memory and context – stores past interactions or knowledge for personalized behavior.
- Orchestration – manages multi-step workflows or multi-agent collaboration.
- Governance and monitoring – tracks performance, prevents errors, and ensures compliance.
These components work together to turn static AI models into dynamic, operational assistants.