In an era where digital interactions dominate, the need for intelligent conversational AI has reached unprecedented levels. Enter GreenNode, a leading platform driving this transformation through the seamless fusion of Large Language Models (LLMs) and advanced RAG techniques. With our proprietary GreenNodeLM, purpose-built for Vietnamese language processing, we’ve achieved top recognition at the VLSP 2023 challengchallenge; and we’re continuing to push boundaries with ever more advanced RAG techniques to redefine how AI understands and generates information.

Also read: From Data to Benchmarks: GreenMind becomes Vietnam’s First Reasoning LLM on NVIDIA NIM
Understanding the RAG System
At the heart of GreenNode's AI revolution lies our advanced RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) system, a sophisticated framework that elevates chatbot interactions to new heights. But what exactly is RAG, and how does it transform a simple chatbot into an intelligent conversational agent?
RAG is a hybrid model that merges the best of both worlds: the deep understanding of language from LLMs and the vast knowledge encoded in external data sources. By integrating these two elements, RAG-powered chatbots can deliver precise, relevant, and context-aware responses to users. The system works in two main phases: first, by retrieving information related to the user's query from a diverse range of datasets, and second, by generating a response that's not only accurate but also feels naturally conversational.
The transformation from a Naive RAG approach to our Advanced RAG system includes sophisticated techniques that refine the user's queries through pre-retrieval processing and optimize the final response with post-retrieval enhancements. This dual-action process ensures our chatbots are not just reactive but truly interactive, capable of understanding subtleties and complexities in conversations.
What is a Naive RAG System?
A Naive RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) system represents the most basic implementation of the RAG framework—where a retriever fetches relevant documents based on a user query, and a generator (usually a large language model) produces an answer by simply combining the retrieved text with the prompt.
In this architecture, the retrieval and generation steps are loosely coupled, meaning the retriever operates independently without deep contextual understanding of the query’s intent. Typically, such systems use vector similarity search (e.g., cosine similarity in embedding space) to identify relevant passages and then feed them directly into an LLM for response generation.
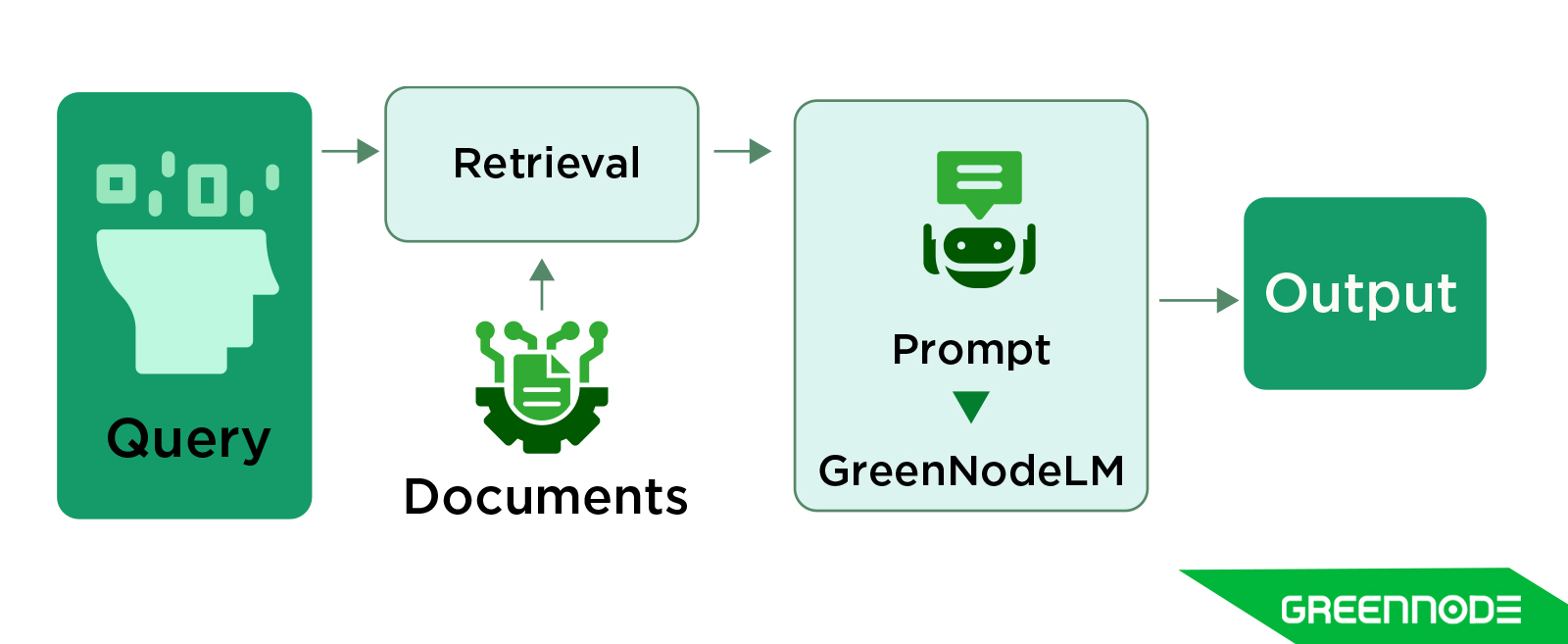
While this approach is easy to implement and cost-effective, it has several limitations:
- Context mismatch: Retrieved documents may be topically related but not semantically aligned with the question.
- Redundancy and noise: Naive retrieval often returns overlapping or irrelevant text, confusing the generator.
- Lack of reasoning: The system doesn’t dynamically refine retrieval or reasoning based on partial responses.
In short, a Naive RAG system provides a functional baseline for retrieval-augmented AI applications but lacks the precision, adaptability, and multi-step reasoning found in more advanced RAG techniques, which leverage context-aware retrieval, feedback loops, and domain-optimized embeddings to dramatically enhance accuracy and relevance.
What is an Advanced RAG System?
An Advanced RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) system builds upon the limitations of naive RAG by introducing context-aware retrieval, iterative reasoning, and dynamic feedback mechanisms that significantly improve the accuracy and relevance of AI-generated responses.
Unlike naive RARAG, where retrieval and generation are separate processes, an advanced RAG system establishes a tight feedback loop between the retriever and generator. The model doesn’t just retrieve once; it refines its search iteratively based on intermediate outputs, ensuring that the most relevant, high-quality, and semantically aligned information is surfaced.
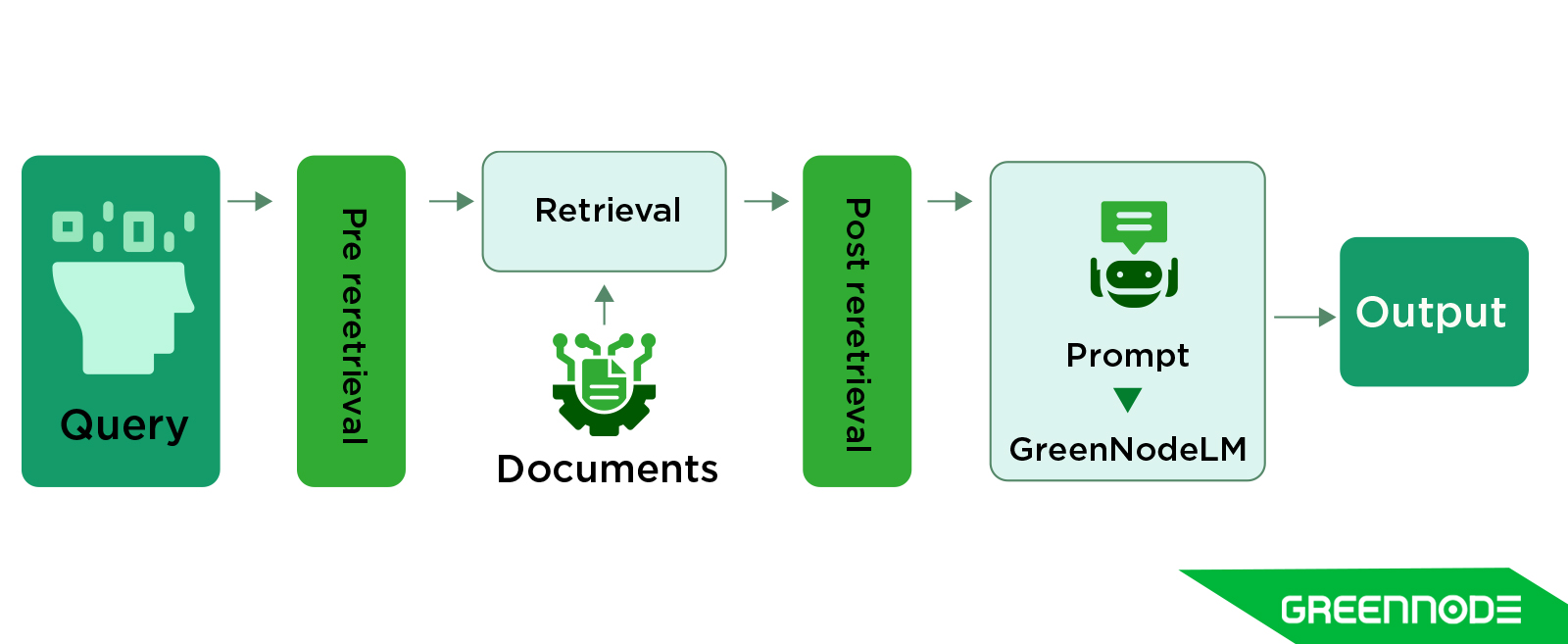
Key characteristics of advanced RAG techniques include:
- Contextual retrieval optimization: The retriever uses embeddings fine-tuned on domain-specific data to improve semantic matching.
- Iterative query refinement: The generator can reformulate queries during inference to retrieve more accurate information.
- Ranking and filtering layers: Advanced RAG systems rank, deduplicate, and filter retrieved passages before feeding them to the LLM.
- Knowledge-grounded reasoning: The generator integrates retrieved knowledge dynamically, improving factual consistency and reducing hallucinations.
- Multi-hop retrieval: Enables reasoning across multiple documents, enhancing complex question answering and long-context understanding.
By combining these advanced RAG techniques, platforms like GreenNode can deliver faster, more factual, and contextually rich responses, making them ideal for enterprise AI assistants, multilingual search, and domain-specific knowledge systems.
Advanced RAG systems mark a major leap from static retrieval pipelines to intelligent, self-optimizing AI architectures capable of learning from feedback and adapting retrieval strategies on the fly.
Also read: Fine-tuning RAG Performance with Advanced Document Retrieval System
Harnessing GreenNodeLM for Advanced RAG Techniques
Building on the success of GreenNodeLM, we’ve embraced the cutting-edge Retrieval Augmented Fine Tuning (RAFT) technique. RAFT is a powerful fine-tuning recipe designed to enhance the model's performance in an "open-book" setting, where the model can refer to documents to answer questions. By training GreenNodeLM to disregard irrelevant retrieved documents and to accurately identify and quote the relevant segments from helpful documents, we significantly reduce distractions and refine the model’s reasoning abilities. This approach has proven to enhance performance across various domain-specific datasets, making our advanced RAG techniques not only smarter but also more adept at handling complex queries in specific fields.
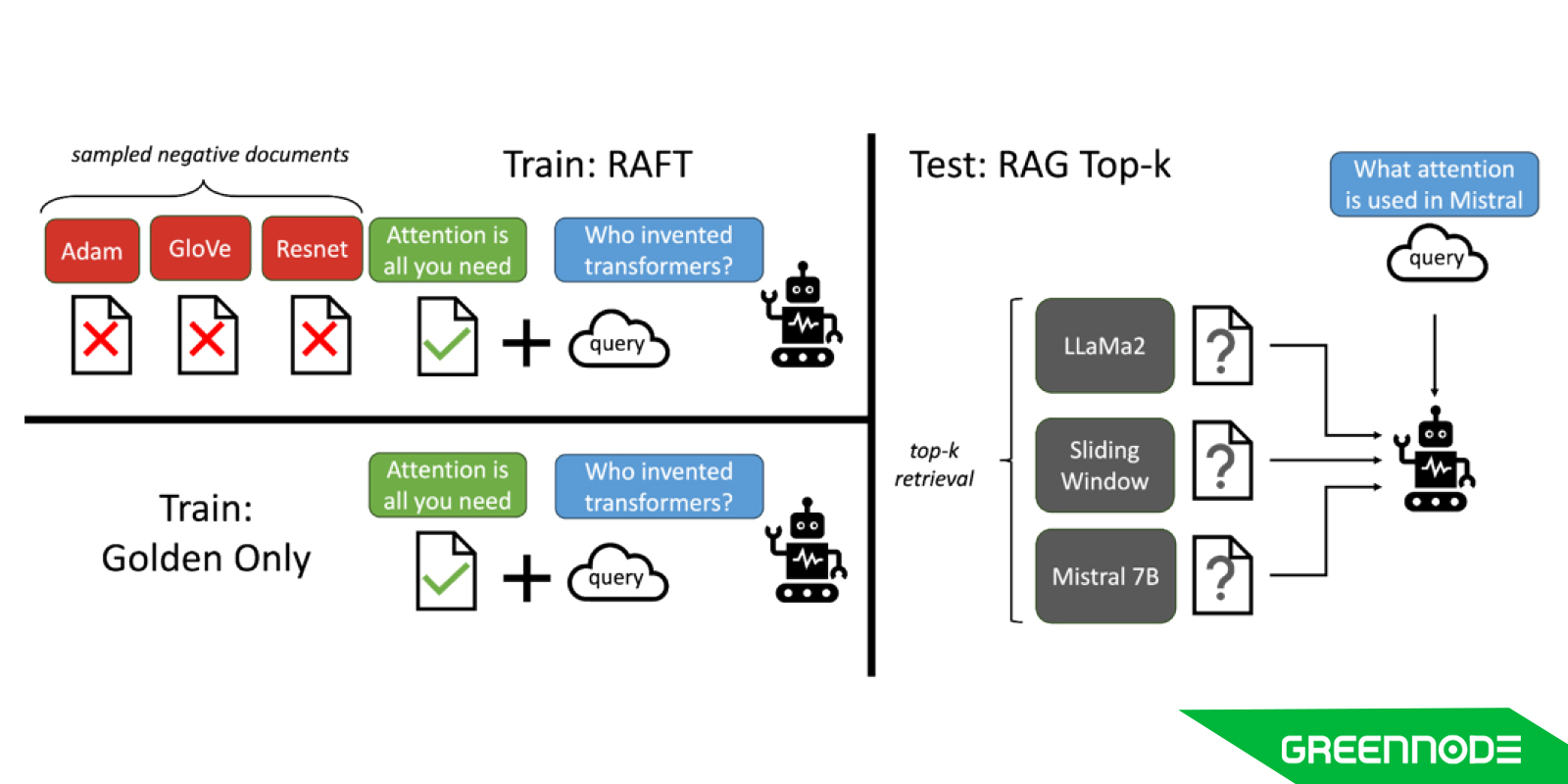
The Power of Pre-Retrieval and Post-Retrieval Enhancements
In advanced RAG systems, performance doesn’t rely solely on retrieval quality, it also depends on how effectively information is prepared before retrieval and refined after retrieval. These two optimization stages, known as pre-retrieval and post-retrieval enhancements, play a crucial role in ensuring that the system delivers highly relevant, accurate, and context-aware results.
Pre-Retrieval Enhancements
Pre-retrieval processes focus on improving the input query and retrieval candidates before the search even begins. By refining the user query or enriching it with contextual cues, the system can dramatically increase the precision of retrieved content.
Common pre-retrieval optimization techniques include:
- Query expansion and re-writing: Automatically reformulating user queries using synonyms, entities, or inferred intent to improve recall.
- Context enrichment: Injecting additional metadata, such as user profile, conversation history, or task domain, to guide retrieval.
- Embedding optimization: Using domain-specific or multilingual embeddings to align semantic meaning across varied data sources.
- Dynamic retrieval strategy: Adjusting retrieval depth or document type based on query complexity or intent.
These pre-retrieval enhancements ensure that the system retrieves the right context—not just the most similar text.
Post-Retrieval Enhancements
Once documents are retrieved, post-retrieval techniques enhance the quality and usability of the data before it reaches the language model. This phase focuses on filtering, ranking, summarizing, and contextualizing retrieved results for optimal generation.
Core post-retrieval enhancement techniques include:
- Re-ranking and deduplication: Prioritizing the most relevant documents and removing noise or overlaps.
- Fact verification and grounding: Cross-checking retrieved data for consistency and factual accuracy.
- Context summarization: Condensing retrieved passages into concise context windows suitable for LLM input limits.
- Knowledge fusion: Integrating multiple retrieved insights into a coherent representation for the generator.
Together, these pre- and post-retrieval processes form the backbone of advanced RAG techniques, ensuring that every stage, from query understanding to final answer generation, is optimized for precision, factual grounding, and contextual awareness.
Real-World Applications - An On-Premise Success Story
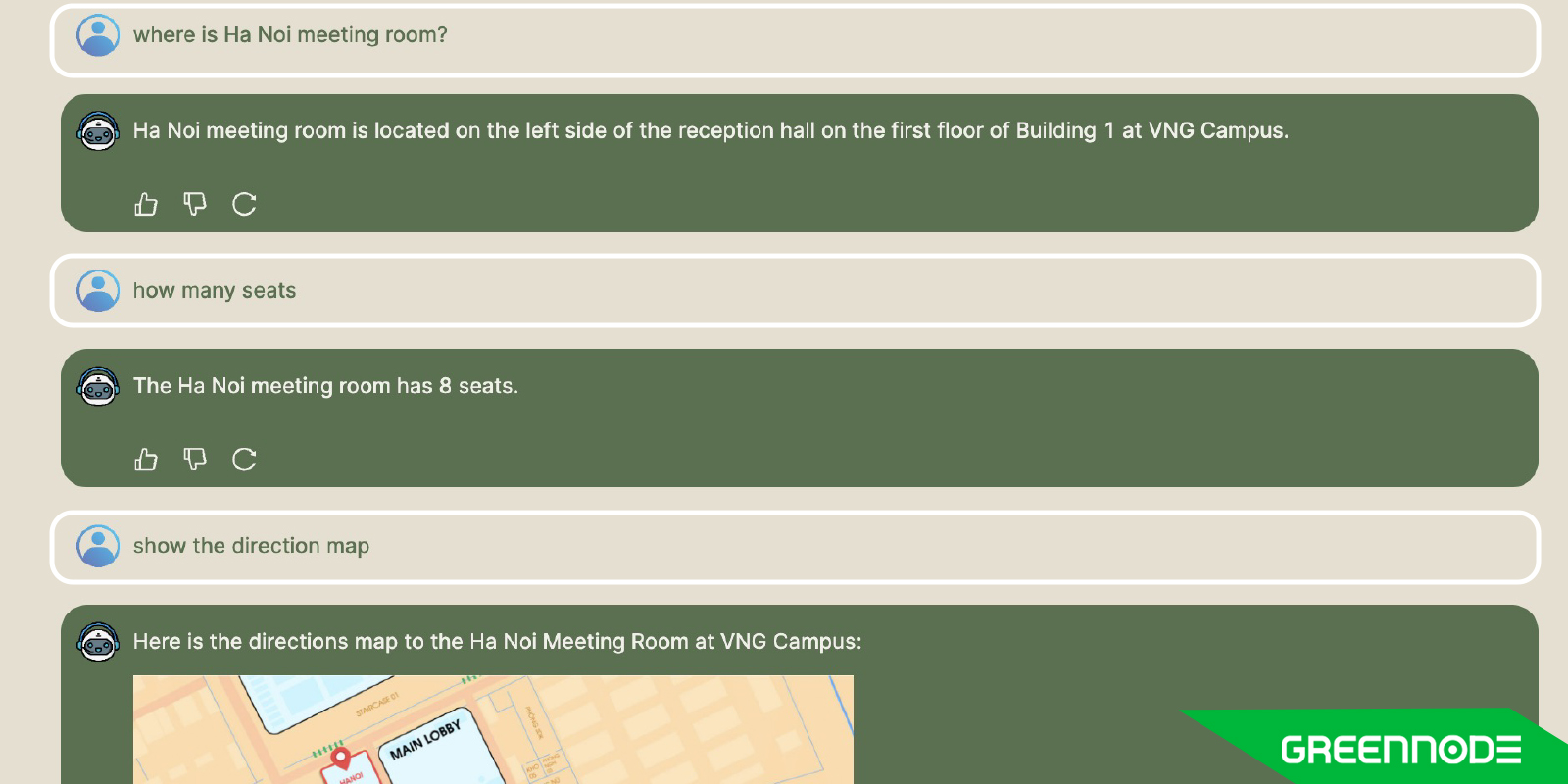
Our on-premise chatbot solution, already deployed within corporate environments, demonstrates our commitment to privacy and user engagement. Employees can interact with the chatbot to access company policies and instructional material, experiencing the direct benefits of an AI that understands the context and delivers relevant information efficiently. The positive feedback we've received is a testament to our solution's ability to enhance workplace productivity and knowledge management.
Looking Ahead
GreenNode is not just about what we’ve accomplished; it's about where we're going. As we look to the future, we’re excited about the possibilities of expanding our offerings to multiple languages and domains. We're dedicated to continuously refining our technology, ensuring that GreenNode remains synonymous with innovation and quality in the conversational AI space.
GreenNode's advanced RAG solution represents a significant leap forward in the realm of conversational AI. By prioritizing accuracy, context-awareness, and user engagement, we're not just creating chatbots; we're creating digital conversationalists—knowledgeable, efficient, and highly intuitive. Join us on this exciting journey as we continue to redefine the boundaries of AI communications.
